 |
| A sun bear takes a nap in one of Free The Bears' hammocks at the Phnom Tamao Wildlife Rescue Center near Phnom Penh. Photo by Erika Pineros. |
Why Cambodia leads the way in rescuing captive bears
Robert Carmichael / CNN | 13 October 2014
 |
| One of Free The Bears' rescued sun bears plays in one of the many enclosures housing over 130 bears at Phnom Tamao Wildlife Rescue Center. Photo by Erika Pineros. |
Cambodia (CNN) -- For Nev Broadis, it's important to act fast when a call comes to rescue a bear cub from the other side of Cambodia.
"There's a vulnerable
animal in distress up to nine or 10 hours away, so there's a sense of
urgency to get there as soon as possible," says Broadis, the regional
director of Australian non-profit Free the Bears. "You put emotions on
hold and start mobilizing -- readying equipment, cages, everything we
might need."
Free the Bears has been
in Cambodia 17 years and in that time has rescued 182 bears, an average
of nearly one a month. Some come from private residences, others from
wildlife traffickers or even garment factories. The condition in which
they find them "is extremely variable."

Sun bear cub 'Jammy'' is weighed at the Bear Quarantine Center at the Phnom Tamao Wildlife Rescue Center.
"Then recently we had one
bear arrive in such bad condition that it died as soon as we moved it
from the crate and onto the operating table -- even though we had five
emergency vets there."
Rescuing Number 182
The bear they raced off
to rescue from the Samlaut district near the Thai border in western
Cambodia was a five-month-old endangered moon bear.
Known by his processing
tag as Rescue Number 182, the male cub was in reasonable shape despite
being somewhat malnourished and carrying an injury thought to have been
inflicted by a snare.
"When the hunters came
along to check the snare, the mum would have left and the hunters would
have taken the bear cub," says Broadis, as he works to pacify the
stressed animal with clucking sounds to imitate its absent mother. "But
there's no sign of any wound or any blood now. It's healed over very
nicely actually."

Nev Broadis tries to calm the moon bear cub, known as Rescue Number 182.
Broadis says most
animals arriving at Free the Bears' sanctuary outside the capital Phnom
Penh are cubs, some of which were intercepted while being trafficked to
so-called "bear farms" in neighboring Vietnam and Laos, where they are
caged and their bile extracted in a painful process.
Bear bile is a source of
Ursodeoxycholic acid, which is used in traditional Chinese medicine to
treat everything from gallstones to muscle aches. Excess stock is used
in toothpaste and shampoo. It's estimated that 13,000 bears are
currently held captive in bear bile farms across Asia.
Broadis reckons that would likely have been this young bear's fate.
Joint Effort
Although on this occasion Free the Bears fetched the cub, that work more often falls on the shoulders of the country's Wildlife Rapid Rescue Team (WRRT), a counter-trafficking program whose operations are supported by U.S. non-profit Wildlife Alliance.
Recently we had one bear arrive in such bad condition that it died as soon as we moved it from the crate and onto the operating table. - Nev Broadis, Free the Bears
The WRRT, which is
comprised of government officials, military police and Wildlife Alliance
staff, operates a hotline for members of the public to report the
illegal trade in wildlife. It also inspects markets, restaurants and
border crossings and runs a network of informants.
In the most recent
quarter, the WRRT carried out more than 60 operations confiscating
hundreds of trafficked animals, among them two moon bears and dozens of
macaques. The bears were taken to the Phnom Tamao Wildlife Rescue
Center, a 2,300-hectare government-owned facility south of Phnom Penh,
where they joined more than 130 bears currently under Free the Bears'
care.
WRRT's proactive approach was lauded recently by wildlife monitoring group TRAFFIC in a report that assessed more than a decade of Asia's trade of live bears and of bear parts such as paws, meat and bile.
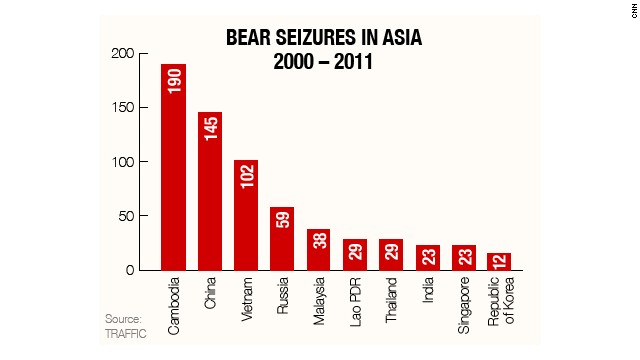 Cambodia leads Asian bear seizures
Cambodia leads Asian bear seizures
TRAFFIC says
Cambodia led 16 other Asian nations in the number of seizures: 190 in
total, of which 156 were live bears. By comparison, Russia, Malaysia,
Thailand, Laos and India managed just 189 seizures between them.
TRAFFIC's data shows
more than 2,800 bears were trafficked in Asia between 2000 and 2011, but
says the true number was far higher. And it warns that three of the
four bears unique to Asia in the Ursidae family -- sun bears, moon bears
and sloth bears -- face "illegal and unsustainable hunting for trade."
Chris Shepherd,
TRAFFIC's regional director for South-East Asia, says the trade "is huge
[and] it's threatening the native bear species." The problem is
compounded by widespread government inaction.
"Enforcement in a number
of places, especially in a number of major trade centers, is really
lacking, if it exists at all," says Shepherd, adding that the solution
lies in large part in better enforcement, education efforts and raising
public awareness -- something that non-profits such as Animals Asia and Free the Bears also undertake.
"When it comes to bears
[Cambodia is] definitely doing more than most -- I mean it's not perfect
but it definitely is a model that's getting results," he says.
A new home
It was early evening
when Broadis and his team arrived back at Phnom Tamao, handing over
Rescue Number 182 to Free the Bears' quarantine center manager Kem Sun
Heng.
Broadis says that on the
way out of Samlaut, a place of subsistence farming and red earth roads
in the foothills of the Cardamom Mountains, he was struck by the fact
that villagers were not surprised to see a bear on the back of a
pick-up. That implies trafficking remains common, he says, "and that's
sad."
Getting Rescue Number
182 back safely after 850 kilometers of appalling roads, on the other
hand, was a relief, partly because the team knows "it's one less bear
going to its death" at a bear bile facility.
"There aren't many moon
bears left in the wild; they've been heavily trafficked to neighboring
countries and their population has been decimated," he says. "So when we
talk about losing an individual, that's important for that particular
species too, whether it's a moon bear or a sun bear."
As Number 182 was coaxed
into his den, the center's two smallest arrivals were snoozing in a
nearby room after a meal of milk. Twin sun bear cubs "Jammy" and "Donut"
were just days old when villagers' dogs scared off their mother from
her nest in Cambodia's remote north-east.
Cambodian keeper Kem Sun Heng feeds sun bear cubs "Jammy" and "Donut."
Taking care of the
endangered bears is a huge challenge not least because while young they
remain vulnerable to infections. But under Heng's expert care, and
three-hourly feeding sessions, the sisters are getting heavier: they are
now eight weeks old and weigh more than four pounds apiece.
"They are good," says
Heng during one feeding session. "They are growing well, they are
healthy, they are eating well and they are very playful."
For his part, Number 182
will spend the coming weeks alone in his den undergoing a battery of
health checks to ensure he doesn't introduce diseases to the rest of the
bear population. Eventually he will be released into a large enclosure
with other rescued moon bears.
"We've put some branches
in there and he's got a hammock and he's got two guys who are going to
look after him, so he'll be fine," says Broadis. "The future's looking
bright for this little cub."


No comments:
Post a Comment